This post was most recently updated on October 19th, 2022
An index is the primary means of organizing and searching documents in Azure Cognitive Search, similar to how a table organizes records in a database. An index is defined by a schema and saved to the search service.
- Method: POST
- URL: https://[name of the search service].search.windows.net/indexes?api-version=[api version]
- Authorization:
Type – API Key
Vale- [Value of the Primary Key]
Add to- Header - Headers:
Content-Type- “application/json”
API-Key – [value of the api key] - Body:
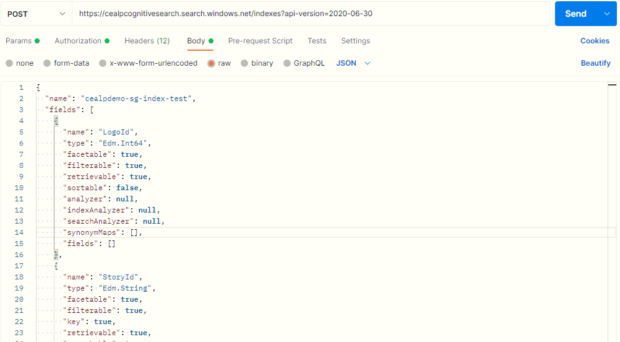
{
“name”: [name of the indexer] (required in case of POST),
“fields”: [ {
“name”: “name of the field”,
“type”: “DataType of the field”,
“facetable”: [true/false],
“filterable”: [true/false],
“retrievable”: [true/false],
“sortable”: [true/false], “analyzer”: null,
“indexAnalyzer”: null,
“searchAnalyzer”: null,
“synonymMaps”: [],
“fields”: [] },……],
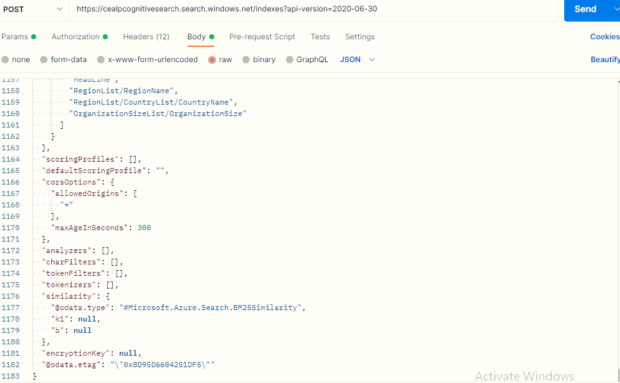
“suggesters”: [ ],
“scoringProfiles”: [ ],
“analyzers”:(optional)[ … ],
“charFilters”:(optional)[ … ],
“tokenizers”:(optional)[ … ],
“tokenFilters”:(optional)[ … ],
“defaultScoringProfile”: (optional) “…”,
“corsOptions”: (optional) { },
“encryptionKey”:(optional){ }
}
N.B.:
- Suggesters support type-ahead queries like autocomplete and for suggestions
- Scoring Profiles are used for relevance tuning
- Analyzers are used to process strings into tokens according to linguistic rules or other characteristics supported by the analyzer
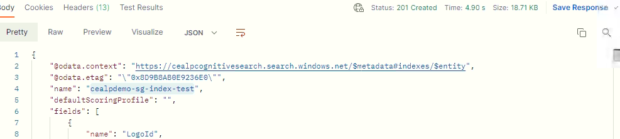
- Response: 201 Created