This post was most recently updated on December 28th, 2016
Event bubbling and event capturing are two ways of event propagation in DOM structure.
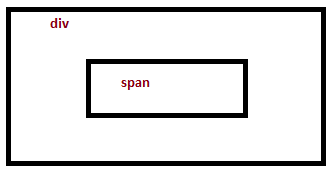
Ex. There are two HTML elements embedded in one another as:
Event bubbling: the event is captured in span element first and then in div.
Event Capturing: the event is captured in div element first and then in span.
Browser Support: In older browsers, some browsers followed bubbling while some in capturing. Although currently all major browsers(IE, FF, Chrome, Safari) support and follow event bubbling.
Enable capturing in Javascript: Javascript currently follow bubbling by default but we can always switch to capturing mode of event propagation. Following is a sample code. View demo here.
Javascript:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
document.getElementById("div1").addEventListener("click", myFunction, true); document.getElementById("span1").addEventListener("click", myFunction1, false); function myFunction() { alert("Hello World2"); } function myFunction1() { alert("Hello World1"); } |
HTML:
|
1 2 3 4 |
<div id="div1"> <span id="span1">This is a span.</span> <p>This is a paragraph.</p> </div> |
CSS:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
div { height: 100px; width: 100px; background: red; } span{ height: 40px; width: 40px; background: blue; } |